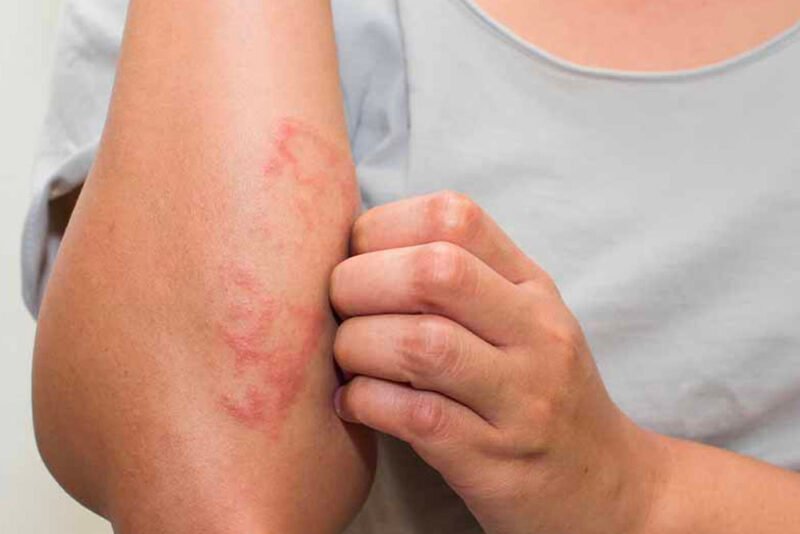
Eczema, a chronic inflammatory skin condition, affects millions of people worldwide, making it a prevalent concern for both children and adults. Characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed skin, eczema can significantly impact one’s quality of life. However, with the right insights, tips, and treatment options, managing eczema becomes more feasible.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the intricacies of eczema, offering valuable insights, practical tips, and effective treatment options for those dealing with this condition.
Understanding Eczema:
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a multifactorial condition influenced by genetics, immune system dysfunction, environmental factors, and skin barrier defects. While it commonly appears in childhood, it can persist into adulthood or develop later in life. Understanding the triggers and underlying mechanisms of eczema is crucial for effectively managing and treating the condition.
Insights into Triggers:
Identifying triggers is a fundamental step in managing eczema. Common triggers include:
- Allergens: Pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and certain foods can trigger eczema flare-ups in susceptible individuals.
- Irritants: Harsh soaps, detergents, fabrics, and environmental factors like extreme temperatures or humidity levels can irritate the skin and worsen eczema symptoms.
- Stress: Emotional stress or anxiety can exacerbate eczema symptoms through the release of stress hormones that trigger inflammation.
- Diet: Certain foods, such as dairy, eggs, wheat, and soy, may exacerbate eczema symptoms in some individuals. Keeping a food diary can help identify potential triggers.
Tips for Managing Eczema:
Effective management of eczema involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, skincare practices, and environmental adjustments. Here are some practical tips for managing eczema symptoms:
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the skin well-hydrated is essential for managing eczema. Use emollients and moisturizers regularly to maintain skin hydration and strengthen the skin barrier.
- Choose Gentle Skincare Products: Opt for fragrance-free, hypoallergenic skincare products to minimize irritation and sensitivity. Avoid harsh soaps or cleansers that can strip the skin of its natural oils.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid triggers that exacerbate eczema symptoms. This may include avoiding certain foods, using fragrance-free laundry detergents, and minimizing exposure to environmental irritants.
- Practice Good Bathing Habits: Take short, lukewarm baths or showers using gentle, non-soap cleansers. Pat the skin dry gently with a soft towel and apply moisturizer immediately to lock in moisture.
- Wear Soft, Breathable Fabrics: Choose loose-fitting, breathable clothing made from natural fibers like cotton or bamboo to minimize skin irritation.
- Manage Stress: Incorporate stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or mindfulness practices to help manage eczema symptoms.
- Seek Support: Joining support groups or connecting with others who have eczema can provide valuable emotional support and practical tips for coping with the condition.
Treatment Options for Eczema:
While there is no cure for eczema, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment strategies may include:
- Topical Steroids: Topical corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve itching during eczema flare-ups. They are available in different strengths and formulations, depending on the severity of symptoms.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: These non-steroidal medications suppress the immune response and reduce inflammation in the skin. They are particularly useful for treating eczema in sensitive areas such as the face or genitals.
- Emollients and Moisturizers: Regular use of emollients and moisturizers helps hydrate the skin and restore the skin barrier, reducing the frequency and severity of eczema flare-ups.
- Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines may be prescribed to relieve itching and promote better sleep, especially during nighttime itching episodes.
- Phototherapy: Phototherapy, or light therapy, involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision. It can help reduce inflammation and improve eczema symptoms in some individuals.
- Biologic Therapies: For severe eczema that does not respond to conventional treatments, biologic therapies may be considered. These medications target specific components of the immune system involved in eczema.
- CBD Topical Cream: CBD topical cream offers promise for eczema treatment due to its anti-inflammatory and moisturizing properties. Applied directly to the affected skin, it can soothe symptoms like redness, itching, and inflammation while improving hydration. While research on its effectiveness is ongoing, many users report positive results. Consulting with a healthcare professional before use, especially if you have underlying medical conditions or take other medications, is crucial.
In Conclusion
Managing eczema requires a multifaceted approach that addresses triggers, adopts healthy skincare practices, and incorporates appropriate treatment strategies. By understanding the insights, implementing practical tips, and exploring treatment options, individuals with eczema can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment recommendations tailored to your specific needs. With proper management and support, living well with eczema is achievable.









